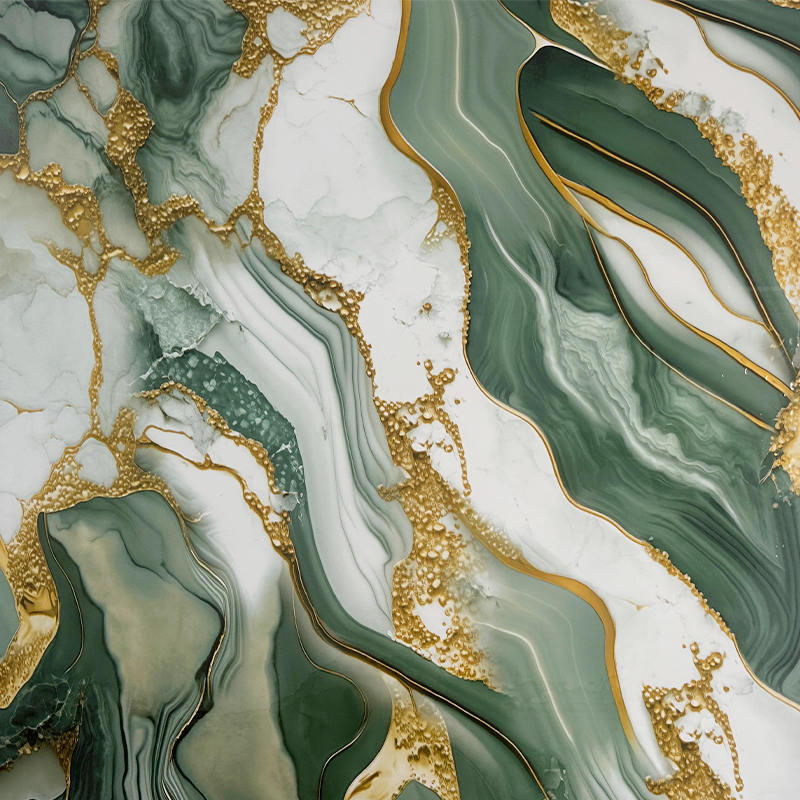
Decorative material film, also known as decorative films or decorative foils, is a versatile, thin-layer material used to enhance the aesthetics and functionality of various surfaces. These films are typically made from polymers, adhesives, and various additives, and are designed to mimic the texture of natural materials, provide protection, or give surfaces a unique visual effect.
Classification and Composition
Decorative material films come in many forms, and their classification is typically based on their primary material, function, and application.
Primary Materials
-
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): This is the most common base material, known for its excellent flexibility, durability, and ease of processing. PVC decorative films can be printed with various wood grain, stone, metal, or other patterns.
-
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): PET films are distinguished by their high transparency, hardness, and wear resistance, and are often used for high-gloss or scratch-resistant surfaces.
-
PP (Polypropylene): PP films are environmentally friendly and non-toxic, frequently used in applications where health and environmental protection are key.
-
Acrylic (PMMA): This material offers an excellent high-gloss effect and a sense of depth, commonly used for high-end cabinet doors or furniture surfaces.
Composition
A typical decorative material film consists of multiple layers:
-
Substrate Layer: Provides the film's basic structure and mechanical strength.
-
Print/Color Layer: Uses high-precision printing technology to give the film a wood grain, stone pattern, fabric texture, solid color, or any other design.
-
Wear Layer/Protective Layer: The outermost, usually transparent layer that resists scratches, abrasion, UV rays, and chemical erosion, extending the material's lifespan.
-
Adhesive Layer: The bottom layer used to firmly bond the film to the substrate.
Key Application Areas
Due to their cost-effectiveness, ease of application, and wide variety of patterns, decorative material films have become an essential material in many industries.
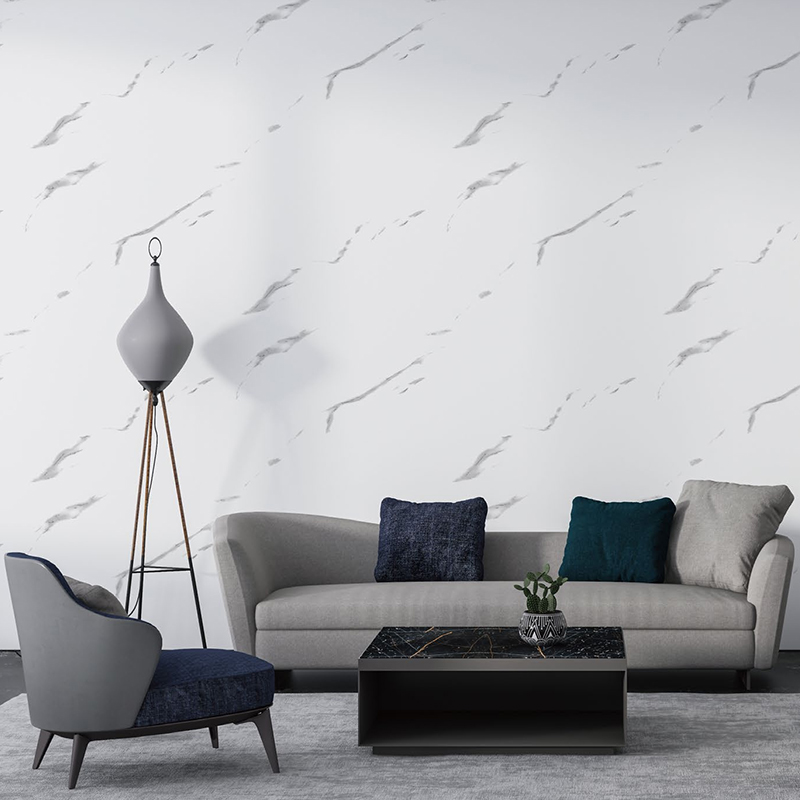
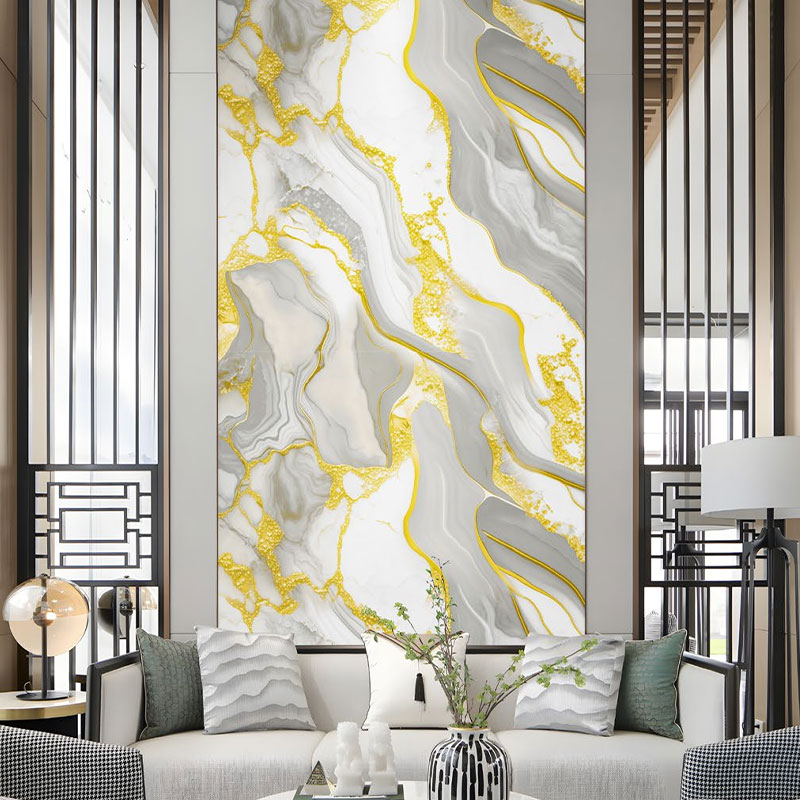
Architecture and Interior Design
In architecture, decorative films are widely used in interior design for:
-
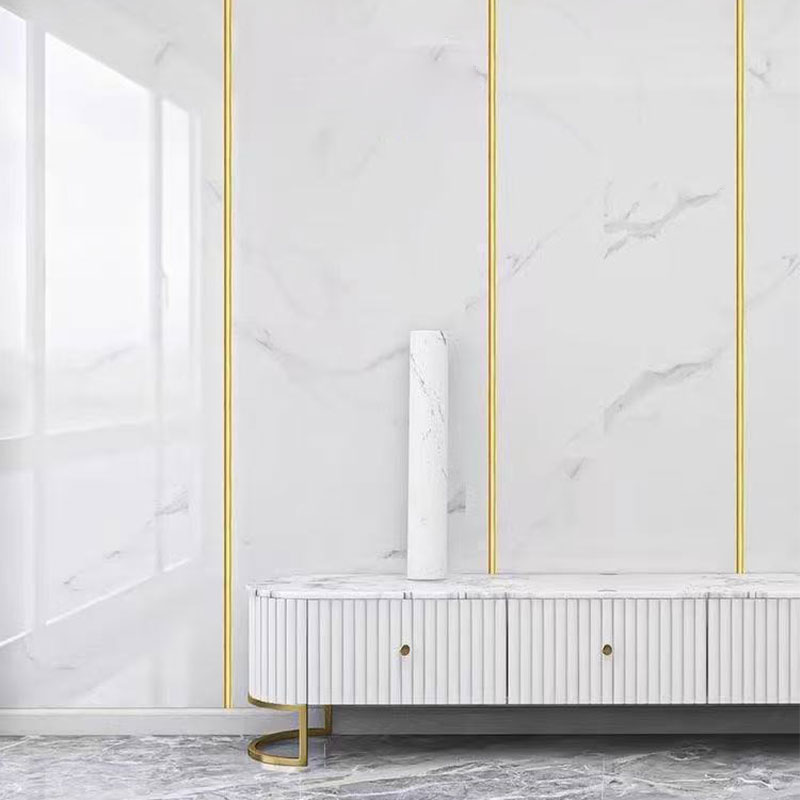
Furniture Surfaces: Used to cover substrates like particleboard and medium-density fiberboard (MDF) to create furniture with the look of wood, metal, or stone. This is also known as finish foil.
-
Wall Decoration: Can be applied directly to walls, replacing traditional wallpaper or paint, to provide a more realistic texture and higher durability.
-
Door and Window Surfaces: Used for renovating doors, window frames, and even elevator cabins, offering a quick and economical transformation.
-
Floor Decoration: Some highly durable decorative films are also used to make flooring.
Automotive and Transportation
The automotive industry also extensively uses decorative films. For example, they are applied to dashboards, door panels, and center consoles to mimic carbon fiber, brushed aluminum, or wood grain, enhancing the vehicle's interior.

Electronics
In the electronics industry, decorative material film is primarily used on phone cases and laptop surfaces to give products a unique visual effect and feel while providing a certain degree of protection.
Advantages and Future Trends
Advantages of Decorative Material Film
-
Cost-Effective: Compared to natural materials like solid wood, marble, or metal sheets, decorative films are significantly less expensive.
-
Easy Application: The installation process is generally simpler and faster than using natural materials.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Some decorative films use eco-friendly materials and reduce the need to exploit natural resources like forests and quarries.
-
Design Diversity: High-precision printing technology can replicate the texture and color of almost any natural or man-made material, offering endless design possibilities.
-
Functionality: In addition to their aesthetic appeal, many decorative films offer special features like resistance to wear, water, and stains, as well as flame retardant and antibacterial properties.
Future Development Trends
With technological advancements, the future of decorative material film will focus more on functionality and sustainability:
-
Integrated Functionality: Future decorative films may integrate more functions, such as self-healing coatings, smart dimming, touch sensitivity, or antibacterial properties.
-
Sustainability: The industry will focus more on using renewable, recyclable, or biodegradable materials to reduce its environmental impact.
-
3D Printing and Personalization: By combining with 3D printing technology, the future may see highly customized decorative films with complex three-dimensional textures to meet personalized market demands.
-
Nanotechnology Application: Nanotechnology can be used to create thinner, more durable decorative films with special optical or physical properties.



 English
English Français
Français русский
русский عربى
عربى Español
Español