The Functional Versatility of Decorative Material Film
Decorative material film has evolved from simple aesthetic overlays into high-performance engineering solutions used across the construction, automotive, and furniture industries. These films are multi-layered synthetic structures—often composed of PVC, PET, or PP—designed to replicate the texture and appearance of natural materials like wood, stone, or metal. Beyond mere decoration, they serve as a protective barrier against moisture, UV radiation, and mechanical wear, significantly extending the lifespan of the underlying substrate while providing a cost-effective alternative to expensive raw materials.
Key Material Composition and Properties
The performance of a decorative film is largely determined by its chemical base. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is widely used for its flexibility and ease of vacuum forming, making it ideal for contoured furniture edges. In contrast, PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) films are favored for their high thermal stability and superior clarity in high-gloss applications. Many modern films now incorporate an "EB" (Electron Beam) cured topcoat, which provides exceptional scratch resistance and an anti-fingerprint finish that is essential for high-traffic commercial interiors.
Core Applications in Modern Manufacturing
The adoption of decorative films has revolutionized how manufacturers approach product design, allowing for rapid prototyping and diverse product lines without the logistical challenges of sourcing natural timber or stone. These films are applied using various technologies, including flat lamination, profile wrapping, and vacuum membrane pressing.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
- Interior Design: Used for wall panels, ceiling baffles, and cabinetry to achieve a luxury aesthetic at a fraction of the weight and cost.
- Home Appliances: Applied to refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines to provide a sleek, metallic, or matte finish that resists corrosion.
- Automotive Trim: Utilized for dashboard overlays and door panels to create wood-grain or carbon-fiber textures that are durable and lightweight.
Comparative Performance Characteristics
When selecting a decorative material film, it is crucial to understand how different types perform under environmental stress. The following table provides a comparison of the three most common film types used in the industry today.
| Feature | PVC Film | PET Film | PP (Polypropylene) |
| Flexibility | Excellent | Moderate | High |
| UV Resistance | Good | Very High | Moderate |
| Eco-Friendliness | Standard | Recyclable | Highly Sustainable |
| Common Finish | Wood Grain/Matte | High Gloss/Mirror | Natural Texture |
Sustainability and Future Trends in Film Technology
As global environmental regulations tighten, the decorative film industry is shifting toward "green" chemistry. This includes the development of phthalate-free PVC and the increasing use of Polypropylene (PP) films, which are halogen-free and emit no toxic fumes when incinerated. Furthermore, the integration of digital printing technology allows for infinite customization, enabling manufacturers to produce small batches of bespoke designs with zero plate-making costs.
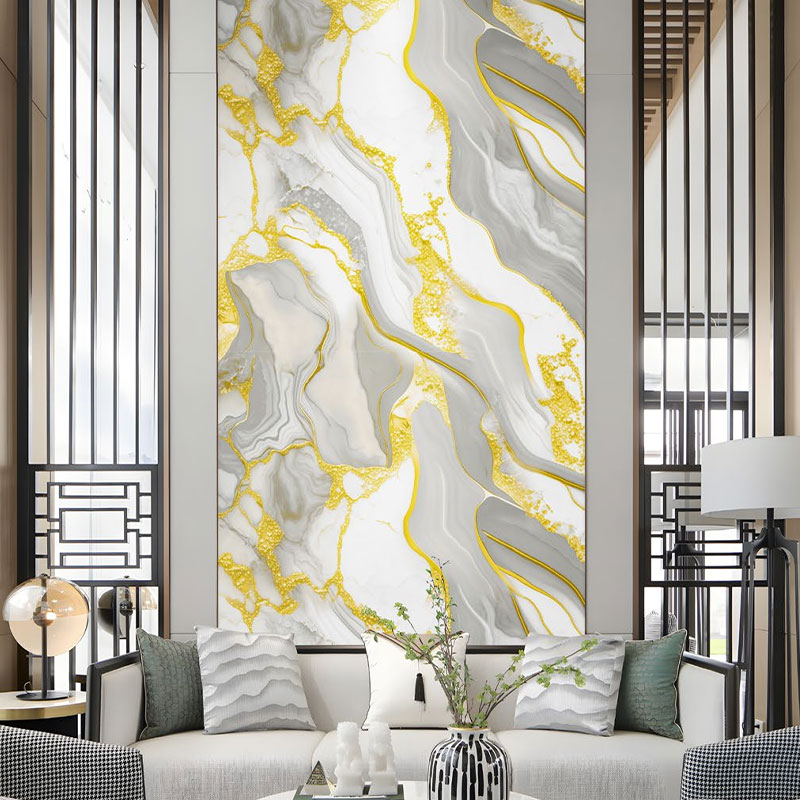

Advancements in Surface Protection
Self-healing decorative films are the latest breakthrough in the market. These films contain a specialized top layer that can "repair" micro-scratches when exposed to heat, maintaining the pristine look of furniture and surfaces for years. Additionally, antibacterial and antifungal additives are being incorporated into the film layers, making them a preferred choice for healthcare environments and public spaces where hygiene is a critical priority.



 English
English Français
Français русский
русский عربى
عربى Español
Español